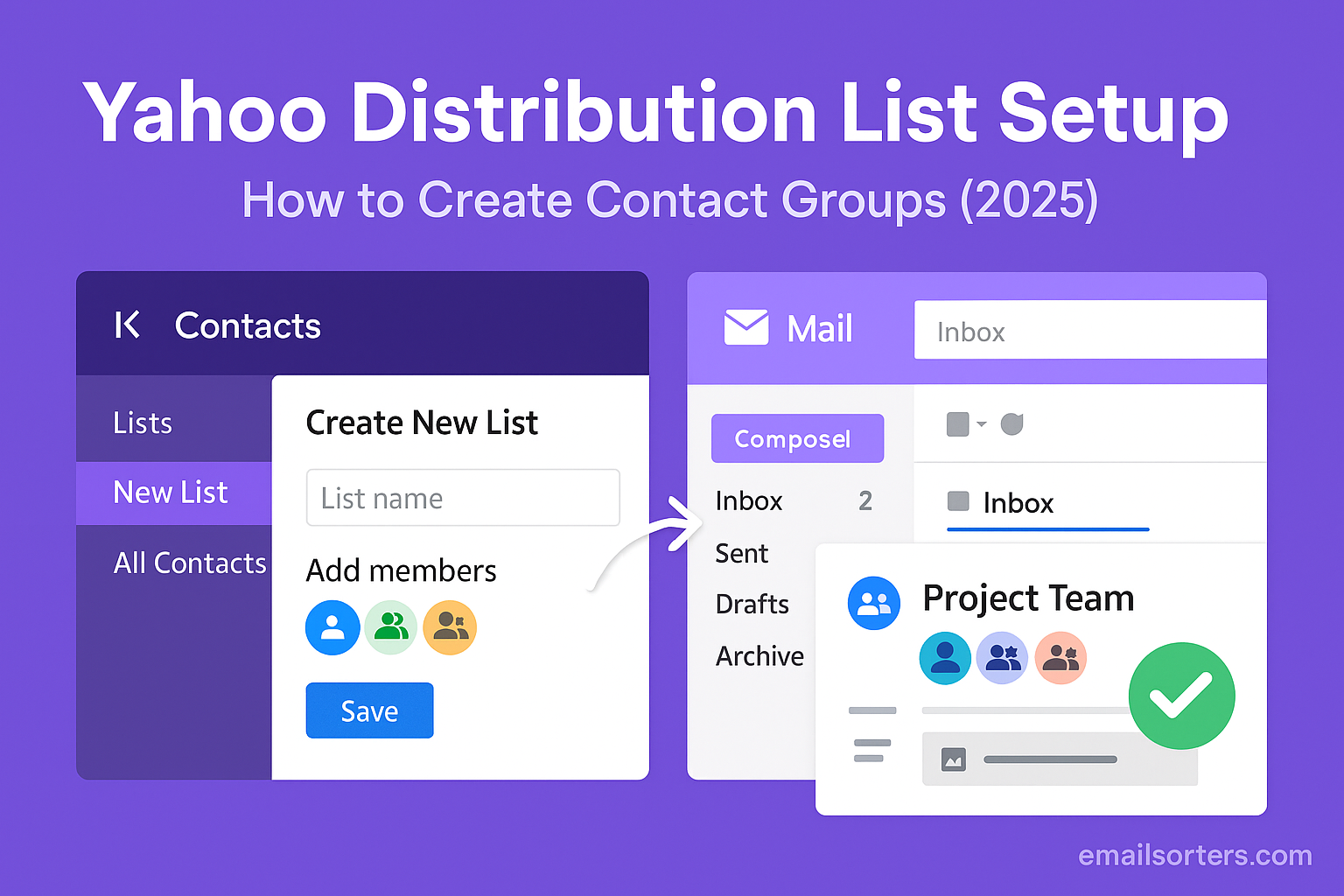
Gmail search by date is the fastest way to dig up old messages without scrolling endlessly. Whether it’s that client email from last year, a receipt you need for taxes, or just a thread you can’t quite remember, date filters make Gmail search way more powerful.
The best part? You don’t need to be a tech expert. With simple commands like before:, after:, or even custom ranges, you can find exactly what you’re looking for in seconds.
In this ultimate 2025 guide, I’ll walk you through how to search Gmail by date, plus pro tips to combine filters for even better results. Ready to master your inbox? Let’s dive in.
The Power of Search: Why Date Operators Are Essential
To use Gmail effectively, one must shift their mindset from manual browsing to targeted searching. Instead of thinking of your inbox as a chronological list, think of it as a powerful database that you can query with specific commands.
Moving Beyond Manual Browsing
The simple act of scrolling back through pages of emails is one of the biggest hidden time-wasters in the digital workplace. The human eye is no match for a computer algorithm designed to sift through millions of data points in a fraction of a second. Learning to use search operators, especially those for dates, replaces inefficient manual labor with precise, instant results.
The Two Systems of Date Search
Gmail provides two flexible systems for thinking about and searching for dates, each with its own set of operators.
- Specific Calendar Dates: This system uses the
after:andbefore:operators with a fixed calendar date. It is perfect for when you know the exact timeframe you need to search, such as “find all emails from last April.” - Relative Timeframes: This system uses the
older_than:andnewer_than:operators with a relative duration (e.g., days, months, years). It is ideal for when you want to search relative to today, such as “find all emails older than two years.”
Mastering the Core Date Search Operators
Understanding the four primary date operators is the foundation of becoming a Gmail search expert. Each one has a specific syntax and purpose.
The after: Operator: Finding Emails Since a Specific Date
The after: operator finds all emails sent or received after a specified date. It is inclusive of the date you enter. The required date format is YYYY/MM/DD. Other formats like MM-DD-YYYY will not work.
- Example:
after:2024/08/15(This will find all emails from August 15th, 2024, to the present day).
The before: Operator: Locating Emails Prior to a Date
The before: operator is the counterpart to after:. It finds all emails sent or received before a specified date. It is also inclusive of the date you enter.
- Example:
before:2024/01/01(This will find all emails from December 31st, 2023, and earlier).
The Power Combination: Searching Within a Date Range
The true power of these two operators is revealed when you combine them to create a precise date range. This is one of the most useful search queries in all of Gmail.
- Example:
after:2025/03/01 before:2025/03/31(This will find all emails sent and received during the month of March 2025).
Using Relative Time with older_than:
The older_than: operator is used for finding mail that is older than a specified duration relative to the current date. The syntax uses a number followed by d (days), m (months), or y (years).
- Example:
older_than:2y(This will find all emails that are more than two years old from today).
Finding Recent Messages with newer_than:
The newer_than: operator is the opposite of older_than:. It finds mail that is more recent than the specified duration.
- Example:
newer_than:7d(This will find all emails from the past seven days).
Advanced Techniques: Combining Date Searches with Other Operators
Date operators are powerful on their own, but they become surgical tools when you combine them with other search parameters.
The Foundation of Powerful Queries
Layering multiple operators allows you to create hyper-specific searches that can find a single needle in a digital haystack. The key is to start with a broad search and add more operators to narrow down the results. For a complete list of all the commands at your disposal, a comprehensive guide to Gmail search operators is an essential resource.
Practical Example 1: Finding a Financial Receipt
Imagine you need to find a specific receipt from an online store for your tax records from the first quarter of last year.
- Query:
from:store@email.com subject:(receipt OR order) has:attachment after:2024/01/01 before:2024/04/01 - Breakdown: This search looks for emails from a specific sender, with “receipt” or “order” in the subject, that have an attachment, all within the specified three-month date range.
Practical Example 2: Locating a Project File
You need to find a presentation a colleague sent you sometime in the last six months for a specific project.
- Query:
from:colleague@email.com has:presentation "Project Apollo" newer_than:6m - Breakdown: This search looks for emails from a specific colleague, containing a presentation file, with the exact phrase “Project Apollo,” all within the last six months.
Practical Example 3: Auditing Communication with a Client
You need to review all communications with a client before a contract was signed on February 1st, 2025.
- Query:
to:client@email.com OR from:client@email.com before:2025/02/01 - Breakdown: This search finds all emails either to or from that client’s specific email address that were sent or received before the contract date.
Using the Advanced Search Interface
For those who prefer not to memorize operator syntax, Gmail provides a user-friendly graphical interface for building advanced searches.
For Those Who Prefer a Visual Menu
In the Gmail search bar, to the far right, there is an icon that looks like a set of sliders or toggles. Clicking this icon will open the Advanced Search dropdown menu. This menu provides fields for all the common search parameters, including “From,” “To,” “Subject,” and a dedicated “Date within” section.
How the Menu Translates to Operators
As you fill out the fields in the Advanced Search menu, you will notice that Gmail automatically populates the main search bar with the corresponding text operators. For example, selecting a start and end date in the date fields will automatically write the after:YYYY/MM/DD before:YYYY/MM/DD query for you. This is an excellent way to learn the syntax of the operators.
Troubleshooting Common Date Search Errors
Sometimes a search does not return the results you expect. The issue is almost always a small error in the query’s syntax.
Incorrect Date Formatting
The most common error is using the wrong date format. Gmail’s search operators require the YYYY/MM/DD format. Using dashes (-), other separator types, or a different order (like MM/DD/YYYY) will cause the search to fail or produce incorrect results.
Misspelling Operators
A simple typo will invalidate the command. Ensure you have spelled after, before, older_than, and newer_than correctly.
Confusing older_than with before
Users sometimes confuse a relative date with a specific one. older_than:1y will find emails that are more than 365 days old from today. before:2024/08/20 will find all emails from before that specific calendar date. They are not interchangeable.
When Your Search Returns No Results
If you are certain an email exists but your search finds nothing, try broadening the date range. If that fails, simplify your query by removing other operators to see if one of them is causing the issue. Finally, remember to add in:anywhere to your query to include the Spam and Trash folders in your search.
Date Searches in the Broader Email Context
Date-based searching is a foundational skill that enhances several other email management tasks, from archival discovery to inbox cleanup.
A Key Tool to Find Old Emails
When you need to dig deep into your archive, date operators are your most precise tool. They allow you to jump instantly to a specific time period without endless scrolling. This makes them a critical component of the strategy to find old Gmail emails.
Locating Unread Mail from a Specific Period
By combining a date search with a status operator, you can perform powerful inbox audits. For example, you can easily find all the unread emails in Gmail from last month by using the query is:unread after:2025/07/01 before:2025/07/31.
Search Capabilities on Other Platforms
While this guide focuses on Gmail, the concept of advanced search is present in other major email platforms. A review of an AOL Mail overview or a Yahoo Mail overview would show that they also offer search tools, although Gmail’s operator-based system is widely considered the most powerful and flexible.
A Checklist for Effective Date Searches
Use this checklist to ensure you are building the most effective and accurate search queries to find exactly what you need.
Your Gmail Search Strategy
This list of questions will guide you from a vague need to a precise, effective search query that delivers instant results.
- Have you identified whether you need a specific date range (
after:/before:) or a relative timeframe (older_than:/newer_than:)? - Are you using the correct and required date format of
YYYY/MM/DD? - Have you considered adding other operators like
from:,subject:, orhas:attachmentto narrow your results? - If you are getting too many results, have you tried adding more specific keywords or a negative keyword (
-keyword) to exclude certain terms? - If you are getting no results, have you double-checked for typos and considered broadening your date range?
- Have you added
in:anywhereto your query to ensure you are searching through Spam and Trash as well?
Managing the Results of Your Search
Finding old emails is often the first step. The next is to take action, whether that means archiving, labeling, or deleting.
Cleaning Up Old Emails
Date operators are perfect for periodic inbox cleanup. For example, running a search for older_than:5y can show you all emails that are more than five years old. You can then select all these messages and delete or archive them in bulk, freeing up space and reducing digital clutter.
Using Third-Party Tools for Bulk Management
For users who need to manage the results of their searches on a massive scale, third-party tools can offer more power than the native interface. Services from companies like Clean Email, for example, can analyze search results and provide advanced, one-click options to bulk-delete, archive, or move thousands of messages at once.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are detailed answers to some of the most common questions users have about searching Gmail by date.
1. How can I search for emails from a single specific day?
To search for emails from one specific day, you need to create a date range that starts and ends on that day. However, the before: operator can sometimes be tricky. The most reliable method is to use after: for the target day and before: for the very next day. For example, to find all emails from August 20th, 2025, you would use the query: after:2025/08/20 before:2025/08/21. This creates a perfect 24-hour window that captures everything from that single day.
2. What is the difference between older_than:1y and using before: with last year’s date?
This is a critical distinction between relative and absolute time. older_than:1y is a floating search. It will always find emails that are more than 365 days old from the day you perform the search. If you run it today, the results will be different than if you run it next month. In contrast, before:2024/08/20 is a fixed, absolute search. It will always find emails from before August 20th, 2024, no matter when you run the query. Use older_than when you need to find things relative to today (e.g., “clean up mail older than 5 years”). Use before when you need to find things related to a specific, historical event (e.g., “find all emails before the project deadline”).
3. Can I use these date search operators on the Gmail mobile app?
Yes, absolutely. The search bar at the top of the Gmail mobile app (for both iOS and Android) is just as powerful as the desktop version. You can type the exact same operators, such as after:2025/01/01 has:attachment, directly into the search bar on your phone or tablet. The advanced search dropdown menu is not present on mobile, so using the text-based operators is the primary method for performing advanced searches on the go.
4. Why does my date search show conversations that started outside my date range?
This happens because of Gmail’s “Conversation View.” By default, Gmail groups all replies into a single, threaded conversation. When you perform a search, the query returns any conversation where at least one message matches your criteria. So, if you search for after:2025/08/01, you might see a conversation that started in July, but it will be included because it contains a reply from August. If you need to find individual messages and not whole conversations, you can temporarily turn off Conversation View in the General Settings.
5. Is there a way to save a complex date search for future use?
Unfortunately, Gmail does not have a built-in “Save Search” feature. However, there are two effective workarounds. The simplest method is to perform your complex search and then bookmark the URL of the results page in your web browser. The search query is stored directly in the URL, so clicking the bookmark will re-run the search instantly. For more advanced users, a text expander application can be used to save complex queries as short snippets (e.g., typing ;qtax could automatically expand to your full quarterly tax receipt search query).