Gmail security protections form a multi-layered defense system, leveraging advanced AI and a secure-by-design infrastructure to safeguard billions of users from digital threats. From the moment an email is sent to the second it lands in an inbox, Google implements a cascade of protocols designed to detect malware, block phishing attempts, and ensure user data remains private. This robust framework operates largely behind the scenes, providing a seamless yet powerful shield for personal and professional communications. For a complete picture of its features, it is helpful to start with a Gmail overview to understand the platform’s full scope.
What Are the Core Pillars of Gmail’s Security?
Gmail’s defensive strategy is not built on a single feature but on several interconnected pillars. These components work together to create a resilient environment that anticipates and neutralizes threats before they can impact the user. The system relies on Google’s massive global infrastructure, cutting-edge machine learning models, and transparent user-facing controls. This combination ensures that protection is both powerful and adaptable, evolving alongside the threat landscape.
Machine Learning-Powered Threat Detection
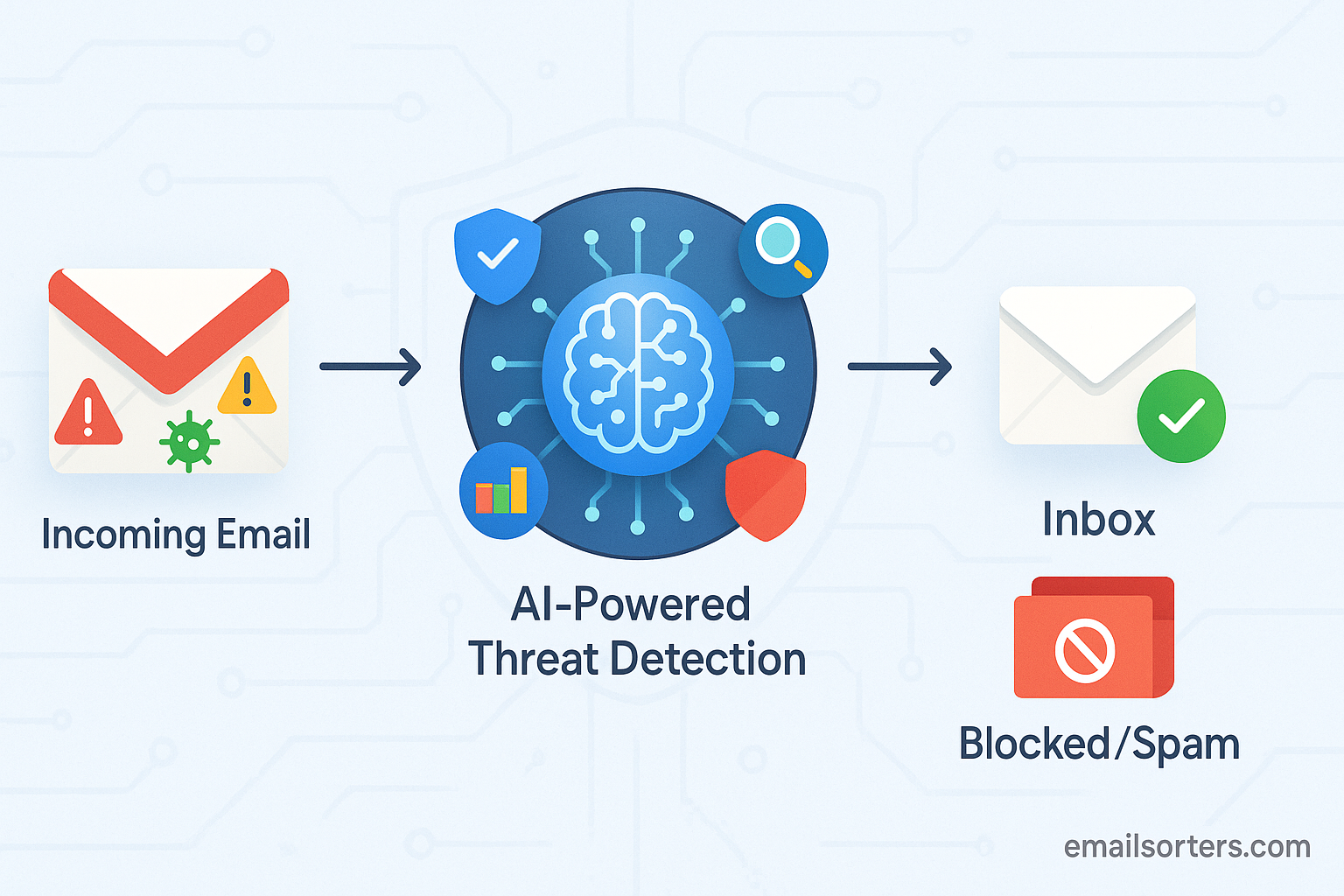
At the heart of Gmail’s defense is a sophisticated machine learning system. This system processes trillions of signals every day to identify and categorize unwanted or malicious content. It is responsible for stopping more than 99.9% of spam, phishing, and malware from ever reaching a user’s inbox. The models analyze countless factors, including sender reputation, link patterns, attachment characteristics, and email content, to make highly accurate predictions. This AI-driven approach allows Gmail to detect novel threats and adapt to the changing tactics of scammer email addresses. It learns from new spam campaigns in real-time, constantly refining its algorithms to stay ahead of malicious actors.
Secure Infrastructure and Encryption
All data within Gmail is protected by a world-class secure infrastructure. Google employs a layered security model that extends from the physical data centers to the application layer. Every email is encrypted while in transit using Transport Layer Security (TLS). This protocol prevents eavesdropping as an email travels across the internet. Once an email arrives, it is encrypted at rest, meaning the data is secured even while stored on Google’s servers. This default encryption ensures that your messages cannot be accessed by unauthorized parties. The platform’s commitment to a secure foundation provides a baseline of protection for every single user.
Proactive Account Safeguards
Gmail also provides proactive tools to help users monitor and control their account security. The system automatically flags suspicious login attempts or unusual activity, sending real-time alerts to the account owner. For example, if a sign-in occurs from an unrecognized device or a new geographical location, Google will prompt for verification. Furthermore, the platform encourages users to perform regular Security Checkups. This guided walkthrough helps users review connected devices, third-party app permissions, and recovery information, empowering them to maintain a strong security posture.
How Does Gmail Protect You From Phishing and Malware?
Phishing and malware represent two of the most significant threats to email users. Gmail employs several specialized mechanisms designed specifically to combat these attack vectors. These protections go beyond simple filtering, actively analyzing content to identify deceptive or harmful elements.

When an email arrives, its attachments are automatically scanned for malware. Google uses a variety of techniques, including signature matching and heuristic analysis, to detect known and emerging viruses. Potentially malicious attachments are executed in a virtual, isolated environment known as a sandbox. This allows Gmail to observe the attachment’s behavior without any risk to the user’s system. If the file attempts to perform a harmful action, it is blocked immediately.
Link protection is another critical component. Gmail automatically checks URLs within emails against Google’s Safe Browsing database, which contains a constantly updated list of dangerous websites. If a link points to a known phishing site or a location hosting malware, Gmail displays a prominent warning before the user can proceed. This serves as a vital safety net, preventing accidental exposure to malicious sites. These automated checks are crucial, as users may also inadvertently sign up for risky newsletters or services with their primary address. Using tools like fake email address generators for non-critical sign-ups can further reduce this exposure.
Can You Enhance Your Own Gmail Security?
While Gmail’s automated systems provide a powerful defense, the most secure accounts are those where users actively participate in their own protection. Google provides several user-controlled features that significantly strengthen account security. Taking a few moments to enable and configure these settings can make the difference between a secure account and a compromised one.
The Critical Role of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
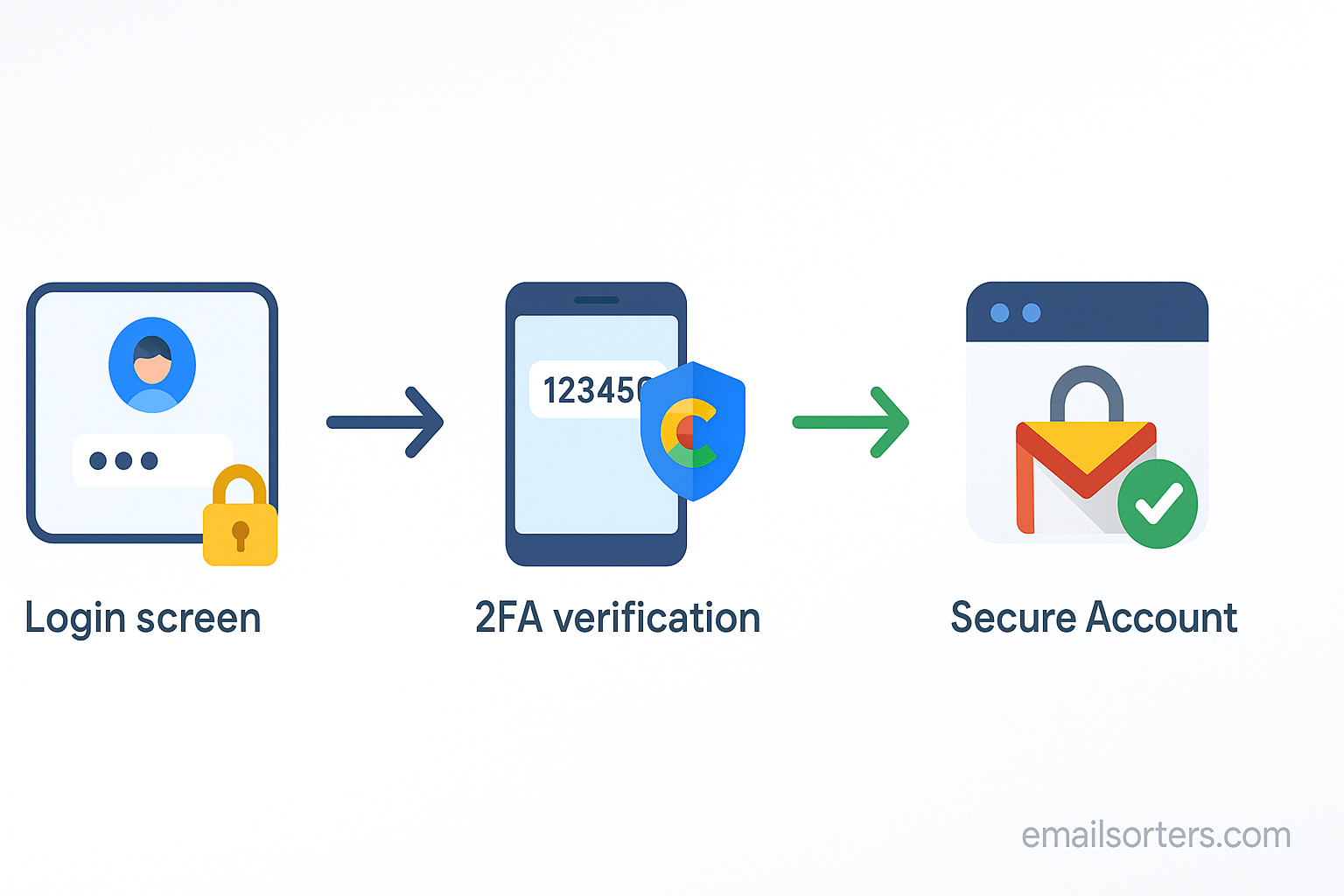
Arguably the single most effective step a user can take to secure their account is enabling two-factor authentication (2FA). This feature adds a second layer of verification to the login process. Even if a malicious actor steals a user’s password, they cannot access the account without the second factor. This is typically a code sent to the user’s phone or a prompt from a trusted device. By requiring something you know (your password) and something you have (your phone), 2FA makes unauthorized access exponentially more difficult. It is a fundamental and essential security measure for any online account.
Using Gmail’s Security Checkup Tool
Google offers a simple, step-by-step tool called the Security Checkup to help users review and manage their account’s defenses. It provides a personalized and actionable set of recommendations to improve security. Completing this checkup regularly is a best practice for maintaining a secure account.
The Security Checkup guides you through several key areas:
- Your Devices: You can review all devices where your Google Account is currently or has recently been signed in. If you see a device you do not recognize, you can immediately sign out of it.
- Recent Security Activity: This section displays recent security-sensitive actions, such as password changes or new sign-ins, allowing you to verify that they were performed by you.
- Third-Party Access: Here, you can see a list of all third-party apps and services that you have granted access to your Google Account data. It is vital to revoke access for any apps you no longer use or trust.
- Your Saved Passwords: The checkup flags weak, reused, or potentially compromised passwords saved in your Google Account, prompting you to update them.
Understanding and Using Confidential Mode
For sending sensitive information, Gmail offers a feature called Confidential Mode. This tool adds an extra layer of control over your sent emails. When you send a message in Confidential Mode, recipients are prevented from forwarding, copying, printing, or downloading the email’s content or attachments. Senders can also set an expiration date for the message, after which it will no longer be viewable. For even greater security, you can require an SMS passcode for verification, ensuring only the intended recipient with the specified phone number can open the message. This feature is a key part of learning how to send secure email directly within the Gmail interface.
Reviewing Third-Party App Access
Over time, many users grant access to their Google Account to various third-party applications and services. While often convenient, each connection represents a potential security risk. A compromised third-party app could potentially expose your data. It is crucial to periodically review which apps have access to your account. Through the Security Checkup or your Google Account settings, you can see a detailed list of these permissions. Revoking access for any applications that are unfamiliar, untrustworthy, or no longer in use is an important step in minimizing your account’s attack surface.
How Does Gmail Fit into the Broader Google Workspace Security?
For businesses and organizations, Gmail is a core component of Google Workspace, a comprehensive suite of productivity and collaboration tools. Within this ecosystem, Gmail inherits even more powerful, enterprise-grade security controls. Administrators gain access to a centralized console to manage security policies, monitor threats, and enforce compliance across the entire organization.
Google Workspace offers advanced threat protection features, such as enhanced phishing and malware detection, specifically tailored for business needs. It includes security sandbox capabilities to analyze attachments in greater depth and protects against sophisticated threats like business email compromise (BEC). Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies allow administrators to create rules that prevent sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or social security numbers, from being shared outside the organization via email. Workspace also supports the use of physical security keys for the most robust form of two-factor authentication available. For organizations evaluating their needs, comparing these built-in features against the best email security software on the market is a valuable exercise.
Advanced Protections and Emerging Threats
The world of cybersecurity is in constant flux, and Gmail’s security team works continuously to deploy new protections against emerging threats. These advanced features often set new standards for the email industry, pushing for a more secure and trustworthy ecosystem for everyone.
Brand Indicators for Message Identification (BIMI)
BIMI is an emerging email standard that helps organizations display their brand logos next to authenticated emails in the inbox. While it may seem like a cosmetic feature, it has significant security implications. For a logo to be displayed, the email must pass strong authentication checks, proving it genuinely comes from the brand it claims to represent. This makes it much harder for phishers to impersonate trusted brands, as their fraudulent emails will lack the verified logo. BIMI provides a clear visual cue of authenticity, helping users quickly identify legitimate messages.
Adapting to New AI-Powered Scams
As artificial intelligence becomes more accessible, malicious actors are using it to craft more sophisticated and convincing phishing emails. These AI-generated scams can be free of the typical spelling and grammar mistakes that once served as red flags. In response, Google is continuously upgrading its own AI models to detect the subtle patterns and contextual clues indicative of these advanced attacks. This ongoing AI arms race means that Gmail’s defenses must constantly learn and evolve to counter the next generation of digital threats.
Data Privacy and User Control
Security and privacy are deeply intertwined. Protecting user data is a core tenet of Gmail’s design. Google’s privacy policies outline how data is used, and the company provides tools like the Google Privacy Center to give users control over their information. It is crucial to understand that while Google scans emails to provide features like spam filtering and Smart Reply, it does not use Gmail content for ad personalization. For those seeking comprehensive protection, understanding both the security features and the privacy controls is essential. The full scope of Gmail security encompasses both preventing external attacks and empowering users to manage their own data responsibly.
Conclusion
Gmail provides a formidable and intelligent security framework that protects users from a vast array of digital threats. Its reliance on machine learning, robust encryption, and a secure global infrastructure establishes a powerful baseline of safety. However, ultimate security is a partnership. By enabling critical features like two-factor authentication, regularly performing security checkups, and remaining vigilant against suspicious communications, users can fully leverage Google’s protections. This combination of advanced technology and informed user action creates the strongest possible defense for your digital life.
Frequently Asked Questions about Gmail Security Protections
1. Is Gmail’s Confidential Mode completely secure?
Confidential Mode adds significant protections by preventing easy forwarding or printing and allowing messages to expire. However, it does not prevent a recipient from taking a screenshot or a photograph of the message. It is best used for adding a layer of control, not for sending top-secret information.
2. Can a Gmail account be hacked even with 2FA enabled?
While 2FA makes it extremely difficult for an attacker to gain access, no system is entirely impenetrable. Sophisticated phishing attacks, known as “man-in-the-middle” attacks, can sometimes trick users into providing their 2FA codes. However, for the vast majority of threats, 2FA is a highly effective deterrent.
3. How often should I perform a Gmail Security Checkup?
It is a good practice to run through the Security Checkup at least every few months. You should also perform a checkup immediately if you notice any suspicious activity on your account or after your credentials have been exposed in a third-party data breach.
4. Does using Gmail on a public Wi-Fi network expose my emails?
Gmail encrypts your connection using HTTPS, which means your data is secure even when using public Wi-Fi. It is always safe to access Gmail through its official website or app. However, be cautious of connecting to fake Wi-Fi hotspots designed to steal information.
5. Will Google ever ask me for my password in an email?
No. Google will never send an unsolicited email asking for your password or other sensitive personal information. Any email that does so is a phishing attempt. Always go directly to the official Google Account website to make any changes.